| Surface Menu | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
Chapter 5. Mill |  |
Figure 5.34. Surface Menu
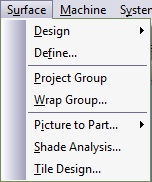
 |
This option is used to create a surface of revolution. The section to be revolved is the marked group from the Group List. The following dialog box appears: Figure 5.38. Revolve Dialogue 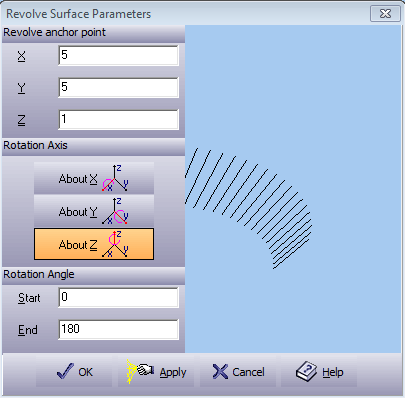 A preview of the rotation section will appear in the box on the right. While editing this dialog box, use options to preview the design before accepting it.
Press to create an rotation surface. Exit without changes by pressing . Press to open the On-line Help. |
 |
To create a drive for a surface, select from the in the menu. The section to be extruded is the marked group from the Group List. The following window appears: Figure 5.39. Extrude Dialogue  A preview of the extrude section will appear in the box on the right. While editing this dialog box, use options to preview the design before accepting it.
Press to create an extrusion surface. Exit without changes by pressing . Press to open the On-line Help. |
 |
Create mathematically definable surfaces. Select this menu item to create the following surfaces through the simple dialog box:
The Range section in the dialog sets the surface boundaries. The range is rectangular, except for the function polar system where the range may be defined by different angle/radius: Figure 5.40. Define Surface Range Input  Define the range of minimal and maximal -> X -> and -> Y -> values to define the patch limits. Press to accept the setting for the surface. Exit without changes by pressing . Press to open the On-line Help. Spherical Surface. To define a spherical surface, select Sphere tab. The Define surface dialog box should look like the dialog box below. Figure 5.41. Define Surface Sphere Dialogue 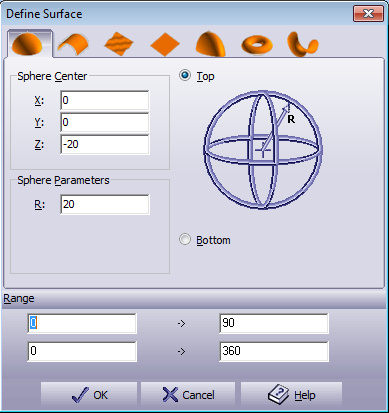
Conical and Cylindrical Surface. To define a conical or cylindrical surface, select the Cone tab. The following dialog box appears: Figure 5.42. Define Surface Cylinder Dialogue 
Function Surface. To define a surface by a function, select Function tab. This option creates a surface by interpreting the given mathematical function. The following dialog box appears:
Planar Surface. To define a planar surface, select Plane tab. The following dialog box appears:
Ellipsoid Surface. To define an ellipsoid surface, select the Ellipsoid tab. The following dialog box appears:
Toroid Surface. To define a toroid surface, select the Toroid tab. The following dialog box appears:
Dual Radius Surface. To define a dual radius surface, select the Dual Radius tab. The following dialog box appears:
|
 |
Project marked groups on either a single or group of surface(s). A new group containing the projected entities is created.
|
 |
Select this option from the menu to wrap a complete geometrical group. Figure 5.49. Wrap Parameters Dialogue 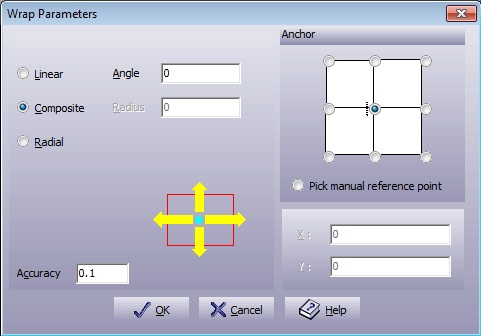
|
 |
Export a surface to Picture to Part. This option enables the Picture to Part to begin the sculpting process on an existing surface. Extract to P2P dialog box shown below: Figure 5.50. Export to P2p Dialogue 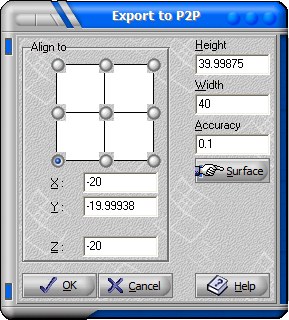
|
 |
Calculates the intersection between Picture to Part surfaces and other surfaces. Depending on the Default Machine Plane, all the surface beneath or above the intersection line will be deleted. |
 |
A wizard for ceramic tile creation. Uses the Shade Analysis function. Mark the geometry of the tile. Select the → command: Figure 5.51. Tile Design Dimensions Dialogue 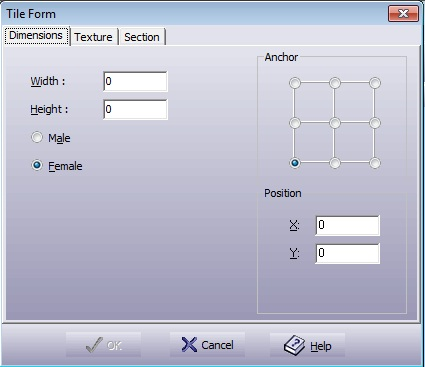
Figure 5.52. Tile Design Texture Dialogue 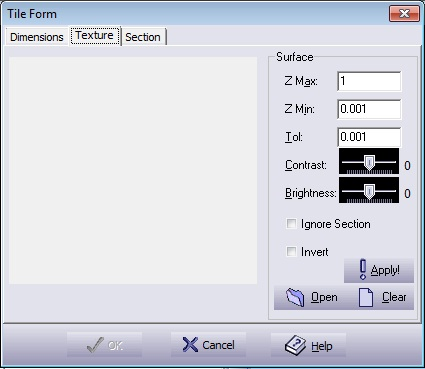
Figure 5.53. Tile Design Section Dialogue 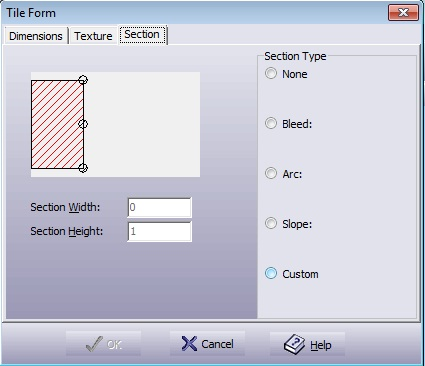
Press to create the surface. |